Unlocking Growth: How Business Orchestration Drives Success
If your workflows are clogged, your growth is capped. Business orchestration clears the path - connecting people, processes, and platforms so your organization can move with purpose. It doesn’t just streamline operations; it unlocks innovation, agility, and speed.
What is Business Orchestration?
Business orchestration is the dynamic coordination of people, data, and systems to deliver seamless outcomes. It ensures every process, person, and platform across your organization is aligned—reducing delays, eliminating friction, and enabling adaptability. Unlike standalone automation, orchestration doesn’t just optimize individual steps. It choreographs entire journeys across departments, technologies, and user needs.
Definition and Meaning
Business orchestration is a holistic discipline that empowers organizations to integrate their workflows, data pipelines, and decision-making processes under a unified control model. It’s about building a flexible, end-to-end operating system that connects siloed tools into a seamless value chain. It goes beyond execution to enforce business rules, embed logic, and create visibility across complex operational landscapes.
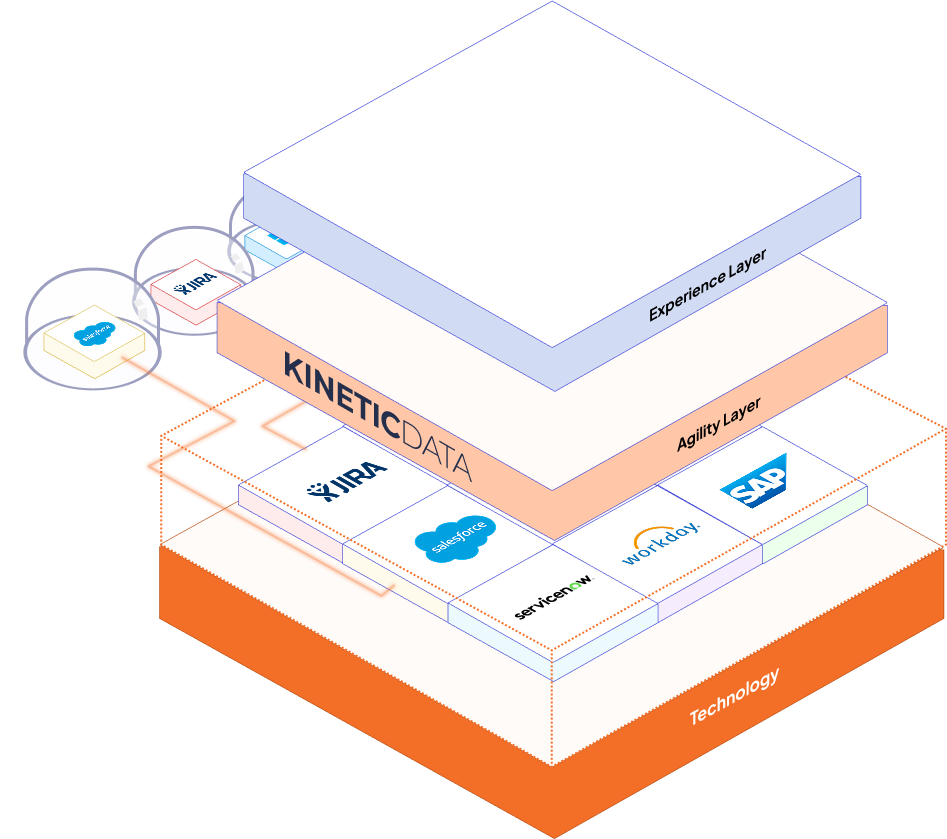
Key Components of Business Orchestration
- Experience Layer – This is where humans meet systems. It includes user-facing interfaces like self-service portals, feedback loops, and status dashboards. Done well, it turns complex backend operations into intuitive front-end interactions.
- Agility Layer – Here lie the business rules, escalation paths, SLAs, and conditional logic that determine how requests are handled. It gives you the power to modify processes without overhauling your entire tech stack.
-
Integrations Layer – This layer manages how systems talk to each other. It handles everything from real-time API calls to asynchronous data pushes, bridging legacy platforms and cloud-native systems alike.
- Foundation & Operations Layer – This underpins everything with the right compliance, performance, and security controls. It includes usage auditing, role-based access, and platform resilience—making orchestration not just agile, but enterprise-ready.
The Importance of Data Orchestration in Business
Data orchestration is a cornerstone of business orchestration. It ensures that the right data reaches the right place at the right time, in the right format. In fast-moving organizations, that can mean the difference between a real-time decision and a missed opportunity. Whether you’re powering dashboards, syncing customer records, or triggering cross-system alerts, data orchestration keeps everything in sync.
Understanding Data Orchestration
Data orchestration involves ingesting, transforming, validating, and distributing data across heterogeneous systems. For example, a customer onboarding flow might involve pulling data from a CRM, validating against financial records, provisioning accounts in multiple SaaS systems, and triggering welcome emails. Without orchestration, this process is brittle, manual, and error-prone. With it, it becomes resilient, responsive, and intelligent.
The Role of a Leader in Data Orchestration
Effective orchestration requires leadership. Technical leaders must set standards for data quality, model governance, and integration design. Business leaders must champion process transparency, data stewardship, and user-centric experience. Orchestration is both a strategy and a capability—it demands alignment across IT and operations.
Business Process Orchestration vs. Automation
Key Differences
Automation is tactical; orchestration is strategic. Where automation handles discrete tasks—approving a form, generating a report—business orchestration ensures the entire journey is governed and optimized.
Benefits of Each Approach
- Automation provides speed, consistency, and cost reduction at the task level.
- Orchestration delivers adaptability, visibility, and resilience across end-to-end business functions.
The smartest organizations don’t choose one over the other—they embed automation within orchestration frameworks to maximize control and flexibility.
Essential Tools for Business Orchestration
Overview of Data Orchestration Tools
Today’s orchestration tools are increasingly composable. The best combine low-code design, real-time integration, and robust governance. They support:
- API-first development
- Event-driven workflows
- Role-based access and audit logging
Examples include Airflow, Dagster, and Prefect for data pipelines; Workato and Tray.io for business integration; and Kinetic Data for mission-critical orchestration with unlimited user and portal scaling.
Best Process Orchestration Software
A great process orchestration platform should:
- Decouple business logic from application logic
- Offer real-time monitoring of flow states
- Scale horizontally across use cases and departments
Kinetic Data distinguishes itself by offering consumption-based pricing—charging only for billable workflows, not for the number of users. It also enables headless orchestration, meaning you can design user experiences independently of backend complexity.
Data Pipeline Orchestration Tools
These tools automate ETL/ELT processes. Key features include:
- Schema validation and transformation
- Data lineage tracking
- Failure handling and retries
Such platforms are vital for analytics, ML pipelines, and real-time data syncing—where accuracy and timing are paramount.
Implementing an Orchestration Layer
What is an Orchestration Layer?
An orchestration layer abstracts business logic from the tools it runs on. Instead of hardcoding process flows into each system, you define them once in the orchestration platform. This allows for:
- Cross-departmental collaboration
- Technology swaps without process rewrites
- Governance that scales with your org
How to Successfully Integrate an Orchestration Layer
- Start with user needs: Design journeys around people, not systems
- Map workflows end-to-end: Include both structured and unstructured steps
- Phase integration rollout: Begin with high-impact connections (e.g., HRMS + ITSM)
- Embed monitoring from day one: Track process health, not just system uptime
Best Practices for Business Process Orchestration
- Use a modular architecture to isolate and upgrade process components
- Employ feedback loops so humans can intervene where needed
- Standardize inputs and outputs with JSON schemas or similar formats
- Use process mining to identify bottlenecks and automation candidates
Effective Workflow Automation Solutions
The goal of automation should be liberation, not just efficiency. A well-designed platform lets non-developers build workflows using visual tools, while offering advanced capabilities for engineers. With Kinetic Data, every workflow can include:
- Dynamic inputs from self-service forms
- Conditional logic and multi-path routing
- Real-time feedback to the user
Strategies for Data Management Orchestration
- Define shared taxonomies across systems (e.g., “customer,” “order,” “region”)
- Use middleware to translate data formats when systems don’t natively align
- Establish roles for data custodianship and compliance checks
- Automate audit trail generation for key workflows

Example 1: Transforming Data Workflows
USDA DISC needed to unify service catalog experiences across multiple mission partners. By implementing Kinetic, they:
- Integrated systems like Jira, Salesforce, and ServiceNow
- Reduced support costs through consistent self-service
- Created a singular, user-friendly cloud services storefront
Conclusion: Future of Business Orchestration
Work isn’t getting simpler—it’s getting more entangled. The winners will be those who orchestrate, not just automate. Orchestration provides the scaffolding to build adaptive systems that flex with market shifts, internal changes, and user needs.
Business orchestration is no longer optional. It’s the mechanism that turns good ideas into repeatable outcomes. It’s how humans and systems move in sync. And in a world where speed, agility, and trust are table stakes—that’s how you win.
