Composable AI Architecture: How to Build Modular AI Systems That You Actually Control
AI models change every few months. Your enterprise workflows shouldn't have to change with them....
Automation integration is a transformative approach that combines various automation technologies to streamline processes and enhance operational efficiency. This comprehensive guide will delve into...

Automation integration is a transformative approach that combines various automation technologies to streamline processes and enhance operational efficiency. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of automation integration, exploring its benefits, essential platforms, and future trends. Readers will gain insights into how automation integration can significantly improve business operations, reduce costs, and foster scalability. Many organizations struggle with disparate systems and inefficient workflows, leading to increased operational costs and reduced productivity. Automation integration offers a solution by creating seamless connections between various applications and processes. This article will cover the definition of automation integration, its key benefits, essential types, leading platforms, implementation strategies, and emerging trends in the field.
Automation integration refers to the process of connecting different automation tools and systems to work together seamlessly, enhancing overall enterprise automation. By integrating various applications, businesses can streamline workflows, reduce manual tasks, and improve data accuracy. This integration allows for real-time data sharing and communication between systems, which is crucial for efficient operations. The primary benefit of automation integration is its ability to create a cohesive environment where different tools complement each other, leading to enhanced productivity and reduced operational costs.
Automation focuses on executing tasks without human intervention, while integration connects different systems to enable them to work together. For instance, robotic process automation (RPA) can automate repetitive tasks, while integration ensures that data flows smoothly between applications. Together, they create a powerful synergy that enhances operational efficiency. Real-world examples include using RPA to automate data entry while integrating it with a customer relationship management (CRM) system to ensure accurate and timely updates.
Integrated automation encompasses several core concepts, including data synchronization, process orchestration, and real-time monitoring. Workflow automation, a subset of integrated automation, focuses on automating specific business processes to improve efficiency. Key principles include defining clear workflows, utilizing APIs for data exchange, and implementing monitoring tools to track performance. Technologies involved in integrated automation include cloud services, middleware, and application programming interfaces (APIs), which facilitate seamless communication between disparate systems.
Further research highlights the foundational methodologies and software products that underpin effective workflow management and automation infrastructure.
Workflow Automation: Process Optimization & Integration Infrastructure
Workflow technology facilitates these by providing methodologies and software to support (i) business process modeling to capture business processes as workflow specifications, (ii) business process reengineering to optimize specified processes, and (iii) workflow automation to generate workflow implementations from workflow specifications. This paper provides a high-level overview of the current workflow management methodologies and software products. In addition, we discuss the infrastructure technologies that can address the limitations of current commercial workflow technology and extend the scope and mission of workflow management systems to support increased workflow automation in complex real-world environments involving heterogeneous, autonomous, and distributed information systems.
Bridging the Digital Divide: How SMBs Can Rival Giants with Low-and No-Code Tools, 2024
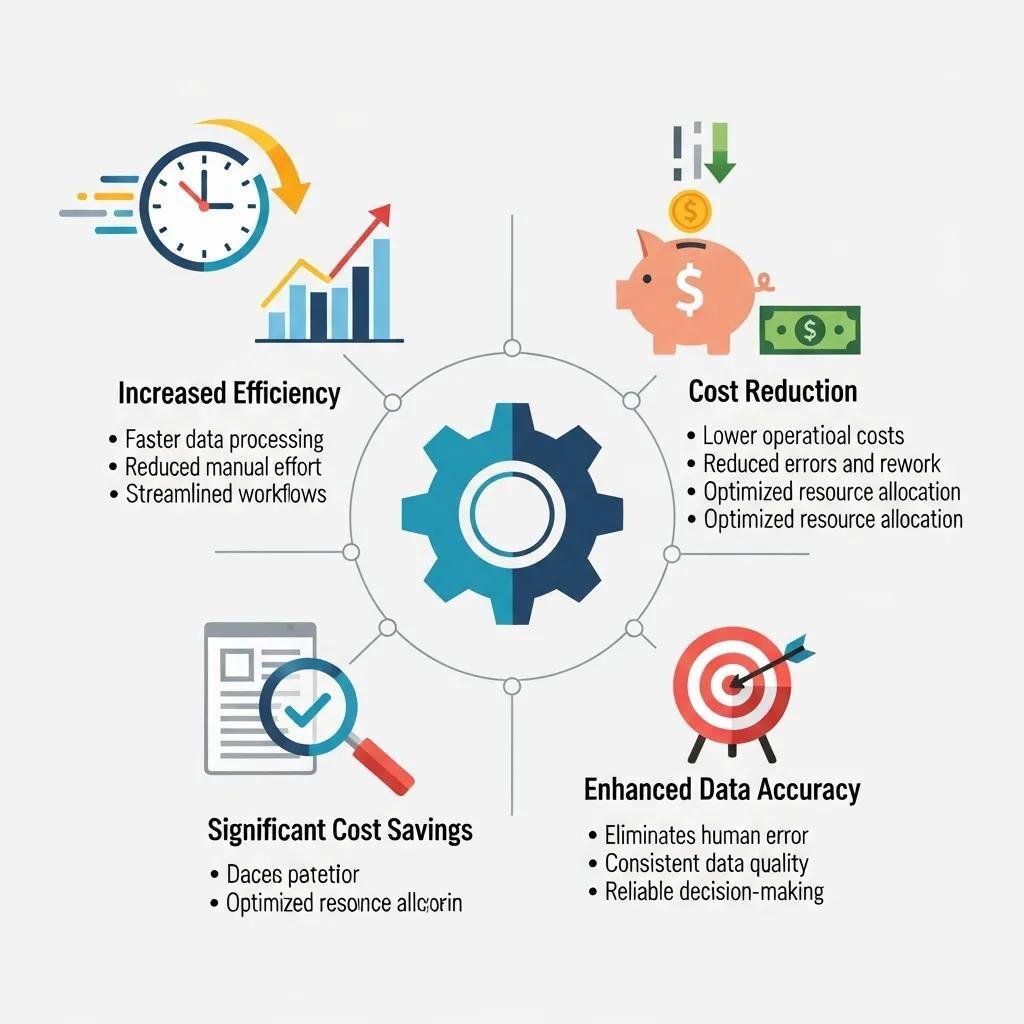
Automated data integration and system integration offer numerous benefits that can significantly enhance business operations. These benefits include improved operational efficiency, cost reduction, and increased accuracy in data handling.
Automation integration streamlines processes by reducing manual intervention, which minimizes the risk of human error. For example, integrating an inventory management system with an e-commerce platform ensures that stock levels are updated in real-time, preventing overselling and stockouts.
Studies indicate that businesses implementing automation integration can achieve operational efficiency improvements typically ranging from 20% to 30%, leading to faster turnaround times and improved customer satisfaction.
By automating repetitive tasks and integrating systems, businesses can significantly reduce operational costs. For instance, automating invoice processing can save time and reduce labor costs associated with manual data entry. Additionally, integrated automation enhances scalability by allowing businesses to easily adapt to changing demands without overhauling existing systems. This flexibility is crucial for organizations looking to grow and expand their operations efficiently.
Modern businesses require various types of automation integration to remain competitive. Key types include data integration automation, robotic process automation (RPA), and application integration.
Data integration automation involves the process of combining data from different sources into a unified view, which is essential for effective decision-making. It plays a critical role in workflow platforms by ensuring that all relevant data is accessible and up-to-date. This integration allows businesses to analyze data more effectively, leading to better insights and informed decisions.
Robotic process automation (RPA) and API-based application integration complement each other by automating tasks and facilitating data exchange between systems. RPA can handle repetitive tasks, such as data entry, while APIs enable seamless communication between applications. For example, an RPA bot can extract data from an email and use an API to input that data into a CRM system, streamlining the entire process.
Several workflow automation platforms and tools are essential for effective automation integration. These platforms provide the necessary infrastructure to connect various applications and automate workflows.
When selecting an Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) solution, businesses should consider factors such as scalability, ease of use, and compatibility with existing systems. Key features to look for include pre-built connectors, real-time data synchronization, and robust security measures. Common pitfalls to avoid include underestimating the complexity of integration and failing to involve key stakeholders in the selection process.
Low-code and no-code automation integration tools empower users to create integrations without extensive programming knowledge. These tools offer several benefits, including faster deployment times, reduced reliance on IT resources, and increased agility in responding to business needs. Popular tools in this category include Zapier and Microsoft Power Automate, which allow users to automate workflows quickly and efficiently.
Research further emphasizes how low-code/no-code tools and iPaaS solutions are democratizing access to advanced automation for businesses of all sizes.
Low-Code/No-Code & iPaaS for Business Automation & Efficiency
This dissertation explores the application of AI-powered automation and low- and no-code tools, specifically focusing on Integrated Platform as a Service (iPaaS) solutions, to empower Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) in the digital marketplace. In a landscape heavily skewed towards large enterprises with substantial resources and access to advanced technologies, SMBs face considerable challenges in achieving operational efficiency, scalability, and customer engagement. This research investigates how tools like Make.com, Zapier, Shopify, and ActiveCampaign, categorized as iPaaS platforms, can democratize access to these capabilities, allowing SMBs to effectively compete with larger competitors. Using PeponiXL as a practical case study, the thesis illustrates the implementation of automation workflows and AI-driven solutions aimed at improving marketing performance, order processing, and
Bridging the Digital Divide: How SMBs Can Rival Giants with Low-and No-Code Tools, 2024
Implementing automation integration strategies requires careful planning and execution. Organizations must identify their specific needs and choose the right tools to achieve their goals.
Best practices for automation integration include defining clear objectives, involving stakeholders from various departments, and conducting thorough testing before deployment. Common challenges include data silos, resistance to change, and integration complexity. Addressing these challenges early in the process can lead to smoother implementation and better outcomes.
Security and compliance are critical considerations in automated data integration. Organizations must ensure that data is protected during transfer and storage, adhering to relevant regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Implementing robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls, is essential to safeguard sensitive information and maintain compliance.

The landscape of automation integration is continually evolving, with several trends and technologies shaping its future. Key trends include the rise of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and hyperautomation.
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing automation integration by enabling systems to learn from data and improve over time. These technologies enhance decision-making processes and allow for more sophisticated automation solutions. For instance, AI can analyze patterns in data to optimize workflows and predict future trends, leading to more efficient operations.
Hyperautomation refers to the use of advanced technologies, such as AI and RPA, to automate complex business processes. This trend is gaining traction as organizations seek to achieve greater efficiency and agility. Hyperautomation can significantly impact enterprise automation by enabling end-to-end process automation, reducing the need for manual intervention, and improving overall productivity.
Further exploration into hyperautomation reveals its potential as a transformative force for organizations seeking end-to-end automated systems.
Hyperautomation: Future Trends, Benefits, and End-to-End Automation
Hyperautomation represents the next evolution of business process automation, combining these tools to create end-to-end automated systems. This paper explores the emergence of hyperautomation as a transformative force in organizations. Following an introduction defining hyperautomation and its enabling technologies, the paper outlines key benefits including accelerated workflows, expanded capacity through digital workers, and enhanced decision-making from AI. Case studies showcase leading companies using hyperautomation to increase efficiency, lower costs, and improve customer experiences.
The rise of hyperautomation: a new frontier for business process automation, AS George, 2023
| Strategy | Mechanism | Benefit | Impact Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Integration Automation | Combines data from various sources | Unified data view for better decision-making | High |
| Robotic Process Automation | Automates repetitive tasks | Increased efficiency and reduced labor costs | High |
| API-Based Application Integration | Facilitates communication between systems | Seamless data exchange and improved workflows | Medium |
This comparison demonstrates how different automation integration strategies can enhance operational efficiency and drive business success.
Automation integration is a vital component of modern business operations, offering numerous benefits that can significantly improve efficiency and reduce costs. By understanding the various types of automation integration, organizations can make informed decisions about the tools and strategies that best meet their needs. As technology continues to evolve, staying abreast of emerging trends and best practices will be essential for businesses looking to thrive in an increasingly automated world.

AI models change every few months. Your enterprise workflows shouldn't have to change with them....

The BPM market is projected to reach $65–70 billion by 2032. Yet roughly 70% of BPM programs never...
Automation solutions are transforming the way businesses operate, enabling them to streamline processes,...